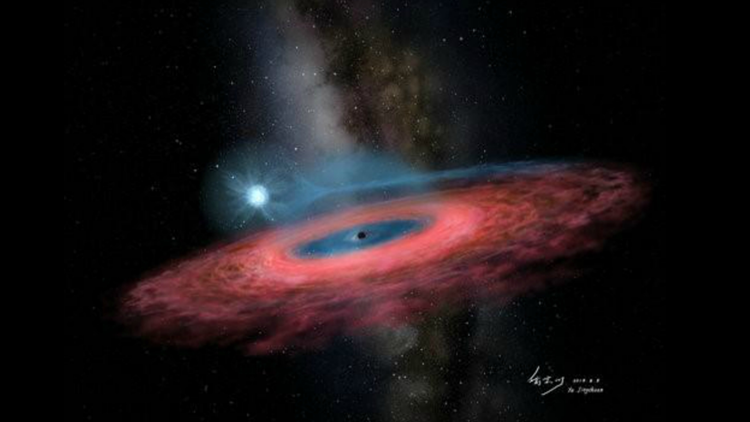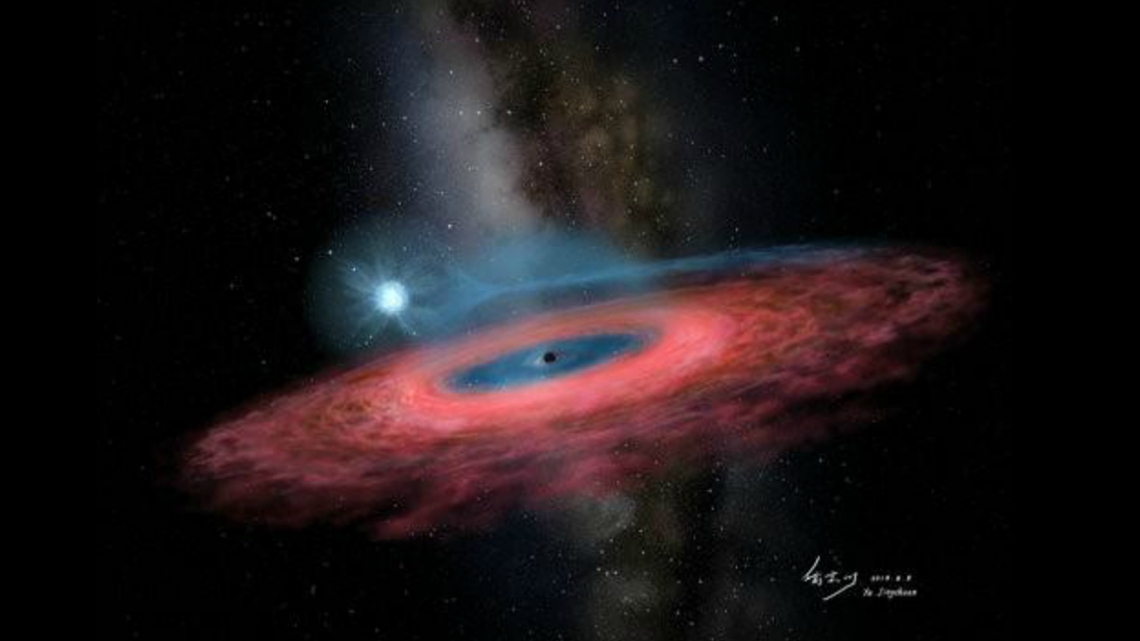
A newly-discovered black hole is so massive, astronomers say it shouldn’t even exist in our galaxy.
CBS News reports Chinese astronomers published their findings this week in the journal Nature. The black hole, named LB-1, is in the Milky Way and is about 70 times the mass of the sun.
Scientists previously thought black holes could only be about 20 times the mass of the sun.
Using the LAMOST telescope in China, scientists found some stars seemingly orbiting an invisible object. Using other telescopes in Spain and the U.S. led astronomers to one star orbiting the black hole every 79 days.
This “dark companion” is 15,000 light-years from Earth.
“Black holes of such mass should not even exist in our Galaxy, according to most of the current models of stellar evolution,” said Prof. LIU Jifeng, who led the research. “We thought that very massive stars with the chemical composition typical of our Galaxy must shed most of their gas in powerful stellar winds, as they approach the end of their life. Therefore, they should not leave behind such a massive remnant. LB-1 is twice as massive as what we thought possible. Now theorists will have to take up the challenge of explaining its formation.”
According to a release about the findings, our Milky Way galaxy has an estimated 100 million stellar black holes, which are formed by the collapse of huge stars. These black holes are so dense, even light can’t escape them.
Prof. David Reitze with the University of Florida said the discovery “forces us to re-examine our models of how stellar-mass black holes form.”